Hafnium oxide deposition (CVD): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
You might notice that Hafnium-Tetrachloride is a solid crystal at room temperature, which is kind of a problem considering that we wanna use it as a vapor in our CVD furnace, in order to react it with oxide for obtaining a Hafnium-Oxide thin film layer. | You might notice that Hafnium-Tetrachloride is a solid crystal at room temperature, which is kind of a problem considering that we wanna use it as a vapor in our CVD furnace, in order to react it with oxide for obtaining a Hafnium-Oxide thin film layer. | ||
===Chemical properties of Hafnium-Tetrachloride=== | |||
[[File:34591.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] | [[File:34591.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 11 October 2022
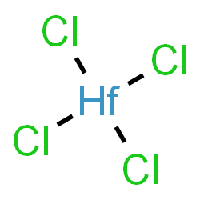
The base of this chemical recipe and processing is Hafnium-Tetrachloride, as it can be seen in the picture.
You might notice that Hafnium-Tetrachloride is a solid crystal at room temperature, which is kind of a problem considering that we wanna use it as a vapor in our CVD furnace, in order to react it with oxide for obtaining a Hafnium-Oxide thin film layer.