Hafnium oxide deposition (CVD): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
To prevent liquefaction of the source before it enters the deposition chamber, maintain the line from the bubbler to the chamber at a temperature of 85°C. | To prevent liquefaction of the source before it enters the deposition chamber, maintain the line from the bubbler to the chamber at a temperature of 85°C. | ||
=== | ===Oxidizer injection=== | ||
[[File:HFO2_CVD_setup.png|200px|right|thumb|CVD setup]] | [[File:HFO2_CVD_setup.png|200px|right|thumb|CVD setup]] | ||
Have O<sub>2</sub> in N<sub>2</sub> in a ration 1:99 | |||
Revision as of 19:34, 13 October 2022
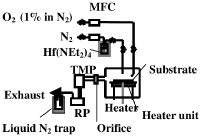
The equipment required for this process are a CVD and a plasma cleaner for removing impurities after the Hafnium oxide deposition
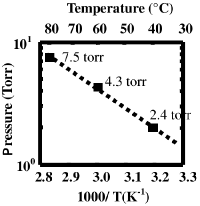
Since HfCl4 is a solid salt at room temperature, we need to first create a liquid precursor, and use direct liquid injection for using it in our CVD.
The process is based on a Japanese paper and requires a complex precursor.
The synthesis of the Hf precursor TDEAH (Hf(NEt2)4) is so complex, that it needs its own page.
Precursor injection
Introduce TDEAH gas into the deposition chamber using a bubbling system, use N2 as the carrier gas.
To prevent liquefaction of the source before it enters the deposition chamber, maintain the line from the bubbler to the chamber at a temperature of 85°C.
Oxidizer injection
Have O2 in N2 in a ration 1:99