Hafnium oxide deposition (CVD): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:34591.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] | [[File:34591.png|200px|thumb|left|alt text]] | ||
HfCl<sub>4</sub> can be produced by several related procedures: | |||
*The reaction of [[carbon tetrachloride]] and [[hafnium oxide]] at above 450 °C;<ref>{{cite book | title = Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology | edition = 4th | year= 1991 | volume = 11}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book| doi = 10.1002/9780470132357.ch41| title= Zirconium and Hafnium Tetrachlorides| series= Inorganic Syntheses| volume = 4| pages = 121| year = 1953| last1 = Hummers | first1 = W. S.| last2 = Tyree, Jr. | first2 = S. Y.| last3 = Yolles | first3 = S. | isbn = 9780470132357}}</ref> | |||
:HfO<sub>2</sub> + 2 CCl<sub>4</sub> → HfCl<sub>4</sub> + 2 COCl<sub>2</sub> | |||
*Chlorination of a mixture of HfO<sub>2</sub> and [[charcoal|carbon]] above 600 °C using [[chlorine gas]] or [[sulfur monochloride]]:<ref>{{cite book | last1 = Hopkins | first1 = B. S. | title = Chapters in the chemistry of less familiar elements | year = 1939 | publisher = Stipes Publishing | page = 7 | chapter = 13 Hafnium}}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last1 = Hála | first1 = Jiri | title = Halides, oxyhalides and salts of halogen complexes of titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium and tantalum | year = 1989 | publisher = Pergamon | location = Oxford | isbn = 978-0080362397 | pages = 176–177 | edition = 1st | volume = 40}}</ref> | |||
:HfO<sub>2</sub> + 2 Cl<sub>2</sub> + C → HfCl<sub>4</sub> + CO<sub>2</sub> | |||
*[[halogenation|Chlorination]] of hafnium carbide above 250 °C.<ref>Elinson, S. V. and Petrov, K. I. (1969) ''Analytical Chemistry of the Elements: Zirconium and Hafnium.'' 11.</ref> | |||
===Processing steps=== | ===Processing steps=== | ||
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100356519C/en | https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100356519C/en | ||
Revision as of 14:44, 11 October 2022
The base of this chemical recipe and processing is Hafnium-Tetrachloride, as it can be seen in the picture.

You might notice that Hafnium-Tetrachloride is a solid crystal at room temperature, which is kind of a problem considering that we wanna use it as a vapor in our CVD furnace, in order to react it with oxide for obtaining a Hafnium-Oxide thin film layer.
Chemical properties of Hafnium-Tetrachloride
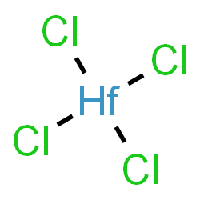
HfCl4 can be produced by several related procedures:
- The reaction of carbon tetrachloride and hafnium oxide at above 450 °C;[1][2]
- HfO2 + 2 CCl4 → HfCl4 + 2 COCl2
- Chlorination of a mixture of HfO2 and carbon above 600 °C using chlorine gas or sulfur monochloride:[3][4]
- HfO2 + 2 Cl2 + C → HfCl4 + CO2
- Chlorination of hafnium carbide above 250 °C.[5]
Processing steps
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100356519C/en
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Elinson, S. V. and Petrov, K. I. (1969) Analytical Chemistry of the Elements: Zirconium and Hafnium. 11.