Hafnium oxide deposition (CVD)
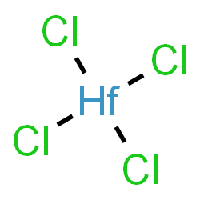
The base of this chemical recipe and processing is Hafnium-Tetrachloride, as it can be seen in the picture.

You might notice that Hafnium-Tetrachloride is a solid crystal at room temperature, which is kind of a problem considering that we wanna use it as a vapor in our CVD furnace, in order to react it with oxide for obtaining a Hafnium-Oxide thin film layer.
Chemical properties of Hafnium-Tetrachloride
HfCl4 can be produced by several related procedures:
- The reaction of carbon tetrachloride and hafnium oxide at above 450 °C;[1][2]
- HfO2 + 2 CCl4 → HfCl4 + 2 COCl2
- Chlorination of a mixture of HfO2 and carbon above 600 °C using chlorine gas or sulfur monochloride:[3][4]
- HfO2 + 2 Cl2 + C → HfCl4 + CO2
- Chlorination of hafnium carbide above 250 °C.[5]
Processing steps
https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100356519C/en
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Elinson, S. V. and Petrov, K. I. (1969) Analytical Chemistry of the Elements: Zirconium and Hafnium. 11.